When modeling real estate projects such as multifamily developments and acquisitions, there are many negative forms of income that should be included. One of the common negative income items included in a model is bad debt.

What is Bad Debt?
Bad debt is a negative income line item that occurs when a payment can no longer be collected because the client, or tenant, is unable to fulfill their obligation due to financial difficulties. Bad debt is an unfortunate cost of doing business and is a risk inherent when working with any customers. In order to underwrite models as accurately as possible, bad debt must be identified and recorded. Bad debt expenses are generally classified as a sales and general administrative expense that can be found in an income statement. Typically, in multifamily real estate deals, one can find it in the revenue section or the EGI. There are two primary ways to calculate bad debt which we will explain below.
How to Calculate Bad Debt
The two methods used to calculate bad debt are the accounts receivable aging method and the percentage of sales method.
Accounts Receivable Aging Method
The aging method groups various accounts by age and uses the different age subsets to determine bad debt for each specific group. The sum of all the groups results in the total bad debt or the estimated amount that is deemed uncollectible. For example, let us say that we have three different groups. One group contains $100,000 of outstanding balances and is 60 days overdue, the second group contains $50,000 and is 30 days overdue, and the third groups contains $30,000 and is less than 30 days overdue. Based on prior knowledge, the first group with an outstanding balance over will have 6% of uncollectible debt, the second will have 3%, and the third will have 1%.

Based on the equation above, the total uncollectible accounts receivable sums to $7,800.
Percentage of Sales Method
The second method, and most popular method used in real estate, is the percentage of sales method. The percentage of sales method is determined by multiplying a flat percentage of sales during a period. For example, during the first period, based on historical data, 3% of the accounts will not be collected and during the second period 1% will also not be collected.
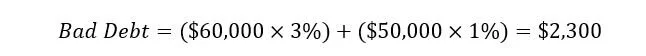

The total bad debt amount is $2,300. At Top Shelf Models, we utilize this approach to determine bad debt. Instead of having different bad debt percentages that apply monthly, like the example above, we have bad debt apply on a yearly basis. Year 1 may be 0.5% and year 2 may be 1% depending on the project.
Conclusion
Bad debt is an inevitable part of doing business regardless of whether the business is real estate or not. There will always be a possibility that when working with a client, they will not be able to fulfill their financial obligations. In order to make your financial model as accurate as possible, one should determine the best method to calculate bad debt and apply it to the model.
